Fundamental Data Structures In JavaScript
Data structures in JavaScript
CODEX
Fundamental Data Structures In JavaScript
Data structures in JavaScript
Here’s a website I created to practice data structures!
directory
Edit descriptionds-algo-official-c3dw6uapg-bgoonz.vercel.app
Here’s the repo that the website is built on:
bgoonz/DS-ALGO-OFFICIAL
Navigation ####Author:Bryan Guner Big O notation is the language we use for talking about how long an algorithm takes…github.com
Here’s a live code editor where you can mess with any of the examples…
Resources (article content below):
Videos
- Abdul Bari: YouTubeChannel for Algorithms
- Data Structures and algorithms
- Data Structures and algorithms Course
- Khan Academy
- Data structures by mycodeschoolPre-requisite for this lesson is good understanding of pointers in C.
- MIT 6.006: Intro to Algorithms(2011)
- Data Structures and Algorithms by Codewithharry
Books
- Introduction to Algorithms by Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein
- Competitive Programming 3 by Steven Halim and Felix Halim
- Competitive Programmers Hand Book Beginner friendly hand book for competitive programmers.
- Data Structures and Algorithms Made Easy by Narasimha Karumanchi
- Learning Algorithms Through Programming and Puzzle Solving by Alexander Kulikov and Pavel Pevzner
Coding practice
- LeetCode
- InterviewBit
- Codility
- HackerRank
- Project Euler
- Spoj
- Google Code Jam practice problems
- HackerEarth
- Top Coder
- CodeChef
- Codewars
- CodeSignal
- CodeKata
- Firecode
Courses
- Master the Coding Interview: Big Tech (FAANG) Interviews Course by Andrei and his team.
- Common Python Data Structures Data structures are the fundamental constructs around which you build your programs. Each data structure provides a particular way of organizing data so it can be accessed efficiently, depending on your use case. Python ships with an extensive set of data structures in its standard library.
- Fork CPP A good course for beginners.
- EDU Advanced course.
- C++ For Programmers Learn features and constructs for C++.
Guides
- GeeksForGeeks — A CS portal for geeks
- Learneroo — Algorithms
- Top Coder tutorials
- Infoarena training path (RO)
- Steven & Felix Halim — Increasing the Lower Bound of Programming Contests (UVA Online Judge)
space
The space complexity represents the memory consumption of a data structure. As for most of the things in life, you can’t have it all, so it is with the data structures. You will generally need to trade some time for space or the other way around.
time
The time complexity for a data structure is in general more diverse than its space complexity.
Several operations
In contrary to algorithms, when you look at the time complexity for data structures you need to express it for several operations that you can do with data structures. It can be adding elements, deleting elements, accessing an element or even searching for an element.
Dependent on data
Something that data structure and algorithms have in common when talking about time complexity is that they are both dealing with data. When you deal with data you become dependent on them and as a result the time complexity is also dependent of the data that you received. To solve this problem we talk about 3 different time complexity.
- The best-case complexity: when the data looks the best
- The worst-case complexity: when the data looks the worst
- The average-case complexity: when the data looks average
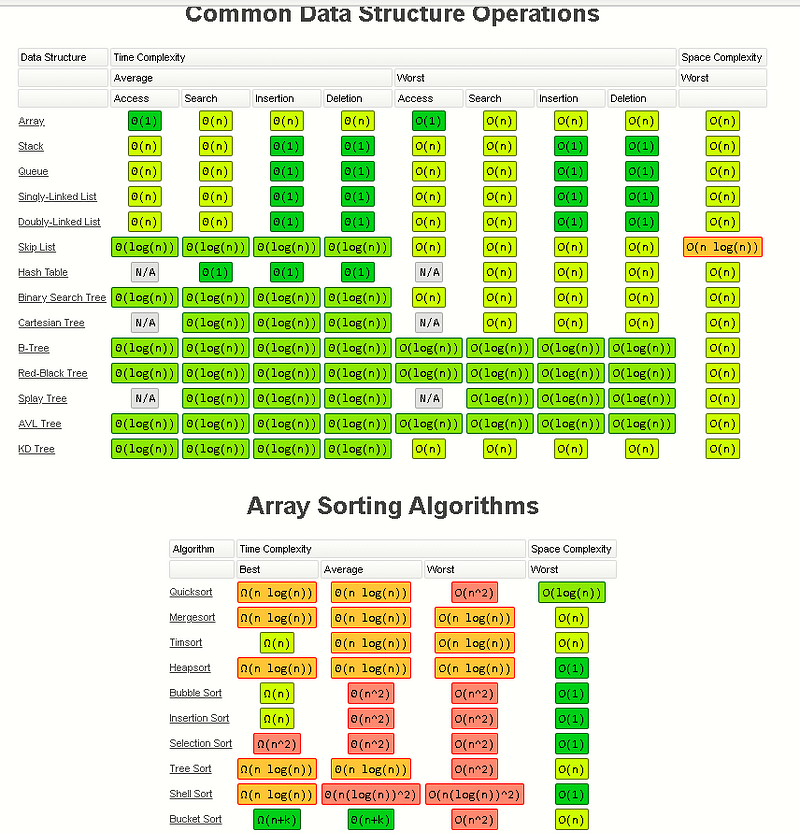
Big O notation
The complexity is usually expressed with the Big O notation. The wikipedia page about this subject is pretty complex but you can find here a good summary of the different complexity for the most famous data structures and sorting algorithms.
The Array data structure
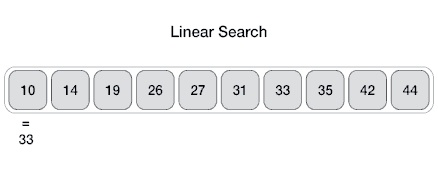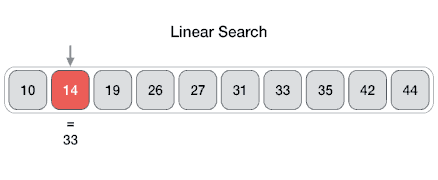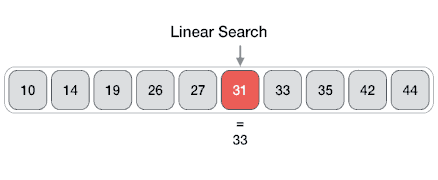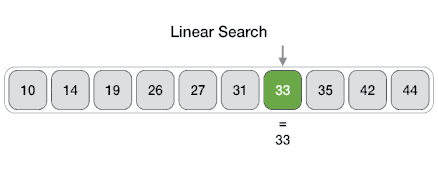
An Array data structure, or simply an Array, is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array. From Wikipedia
Arrays are among the oldest and most important data structures and are used by every program. They are also used to implement many other data structures.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(1) O(n) O(1) O(n)

- The index of an array runs in sequence
- This could be useful for storing data that are required to be ordered, such as rankings or queues
- In JavaScript, array’s value could be mixed; meaning value of each index could be of different data, be it String, Number or even Objects
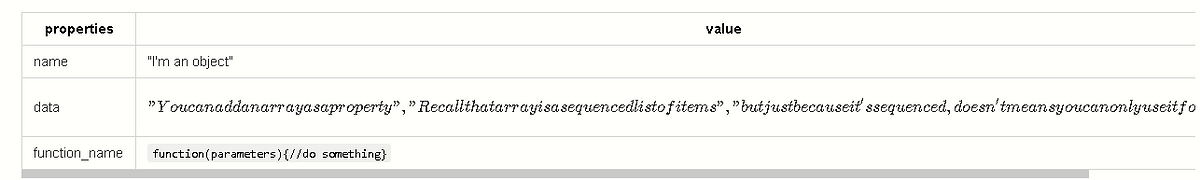
2. Objects
Think of objects as a logical grouping of a bunch of properties.
Properties could be some variable that it’s storing or some methods that it’s using.
I also visualize an object as a table.
The main difference is that object’s “index” need not be numbers and is not necessarily sequenced.
The Hash Table
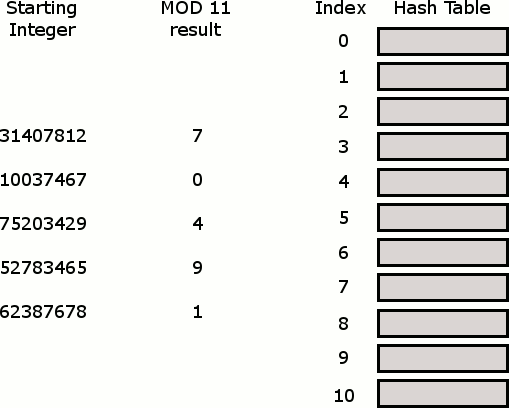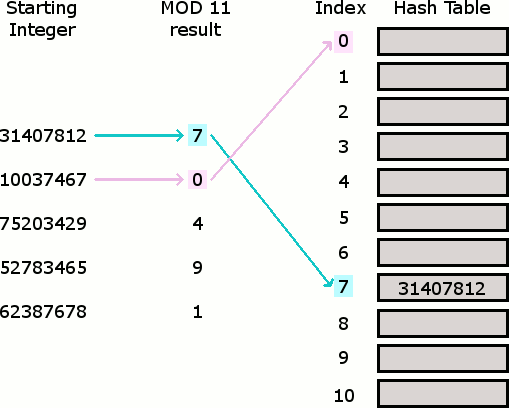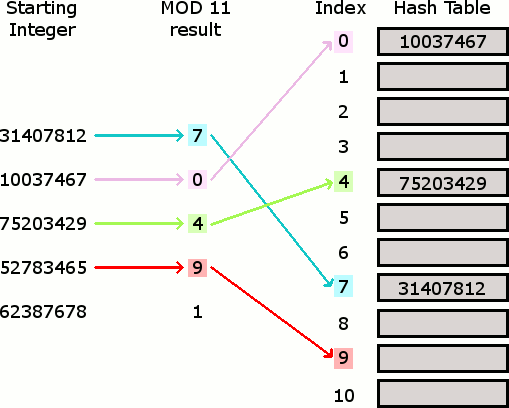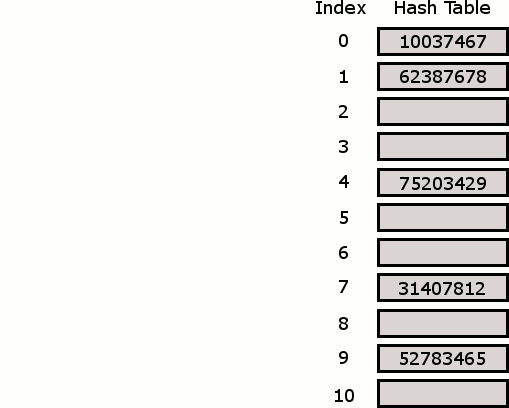
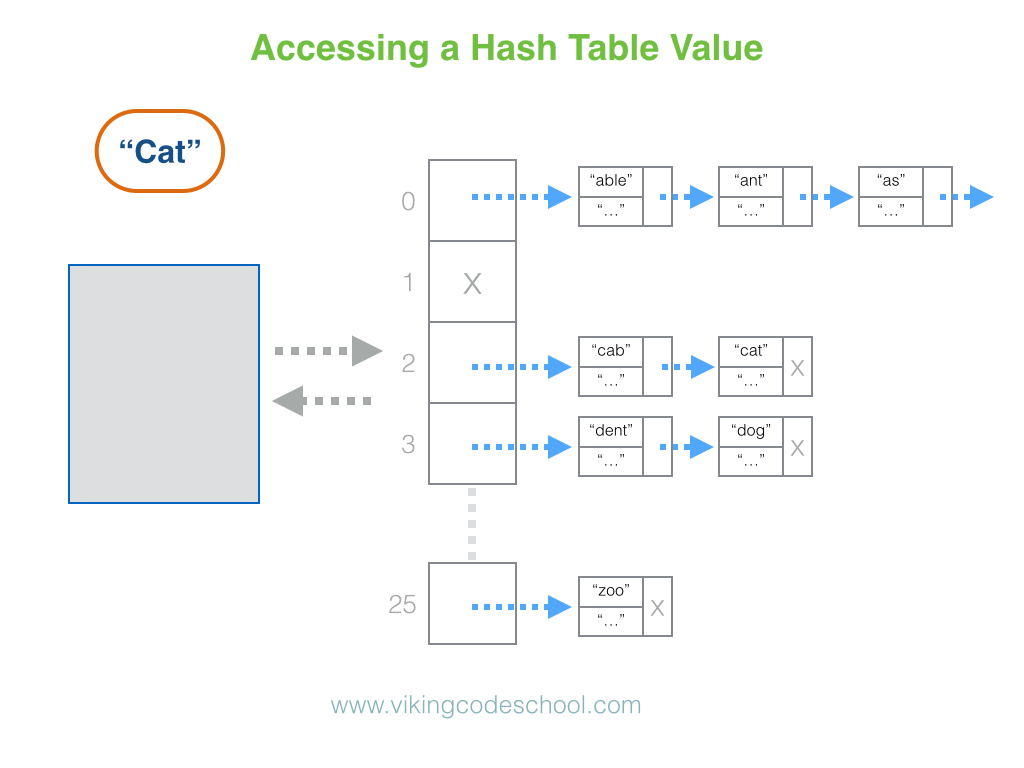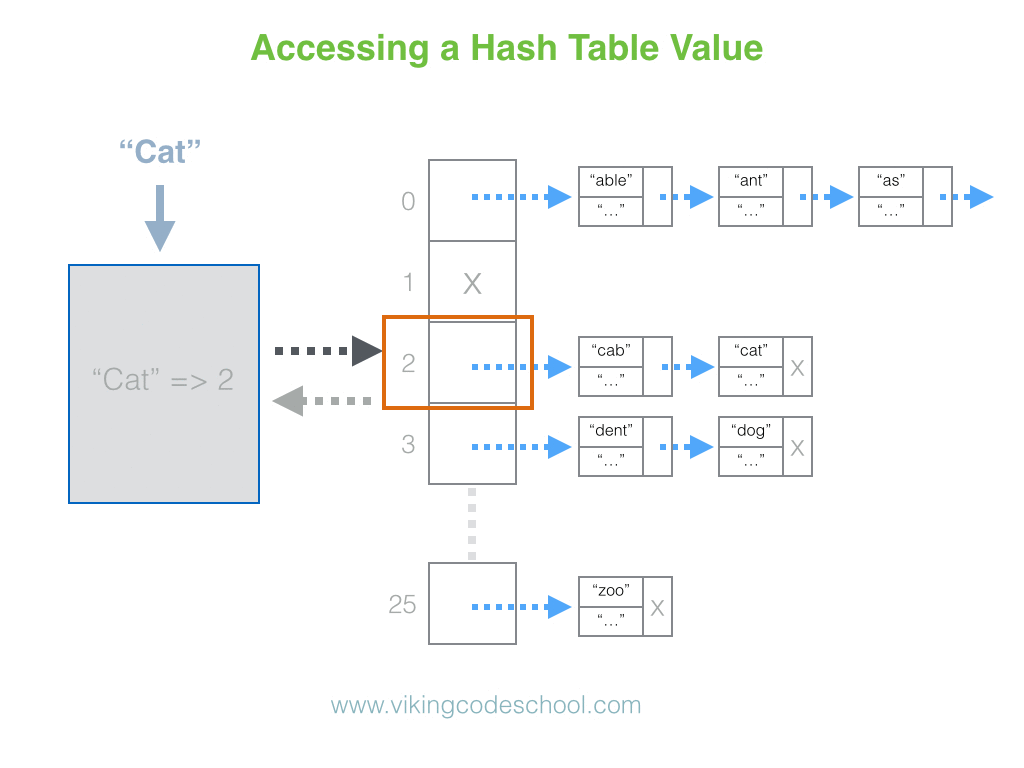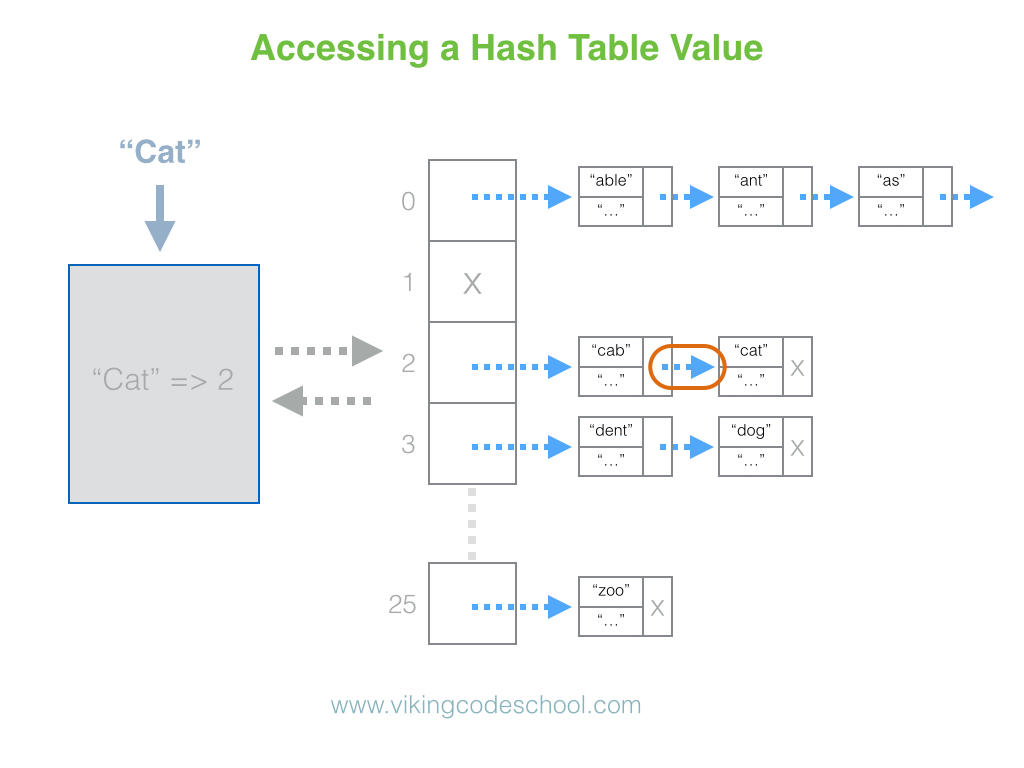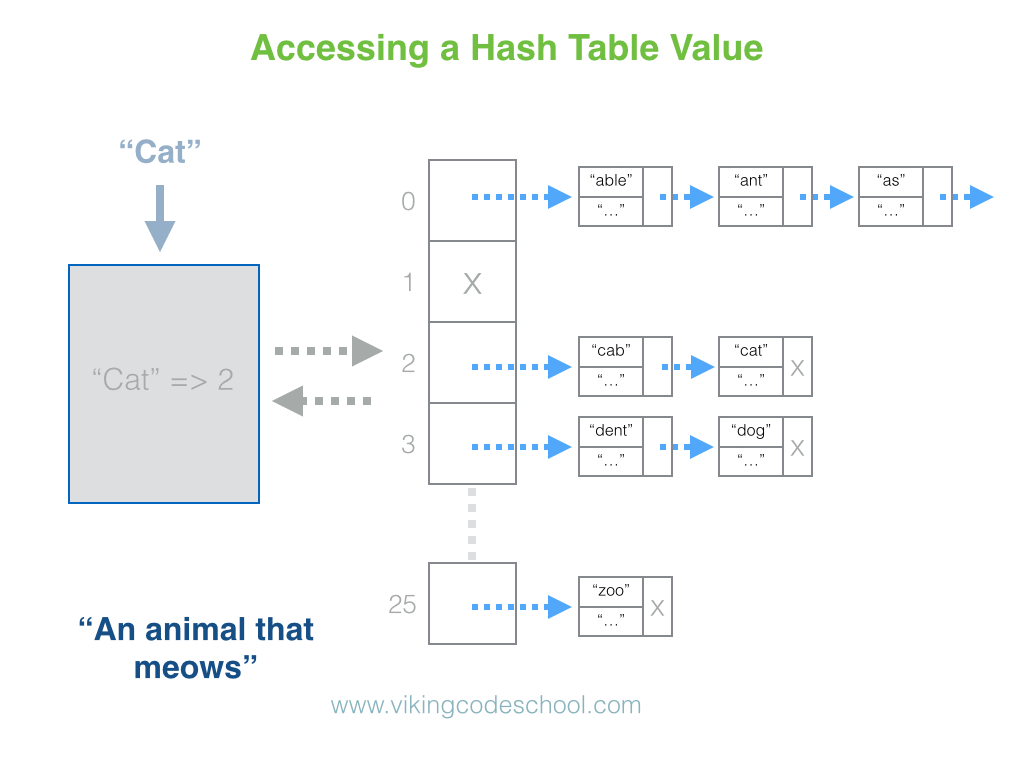
A Hash Table (Hash Map) is a data structure used to implement an associative array, a structure that can map keys to values. A Hash Table uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found. From Wikipedia
Hash Tables are considered the more efficient data structure for lookup and for this reason, they are widely used.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
- O(1) O(1) O(1)
The code
Note, here I am storing another object for every hash in my Hash Table.
The Set
Sets
Sets are pretty much what it sounds like. It’s the same intuition as Set in Mathematics. I visualize Sets as Venn Diagrams.
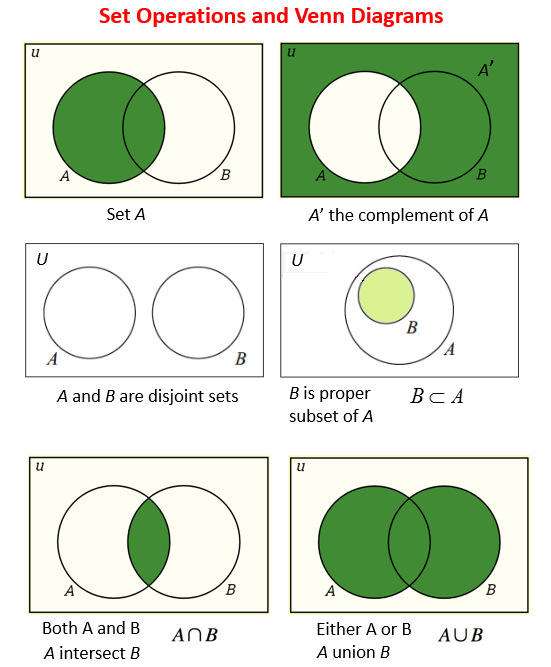
A Set is an abstract data type that can store certain values, without any particular order, and no repeated values. It is a computer implementation of the mathematical concept of a finite Set. From Wikipedia
The Set data structure is usually used to test whether elements belong to set of values. Rather then only containing elements, Sets are more used to perform operations on multiple values at once with methods such as union, intersect, etc…
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
- O(n) O(n) O(n)
The code
The Singly Linked List
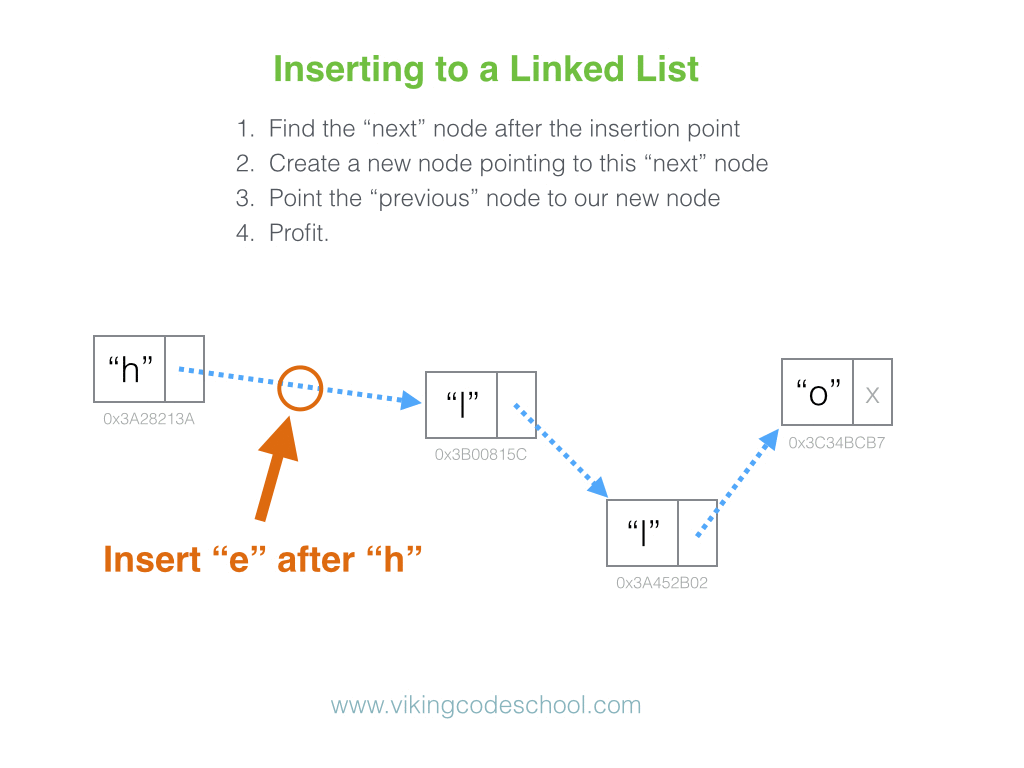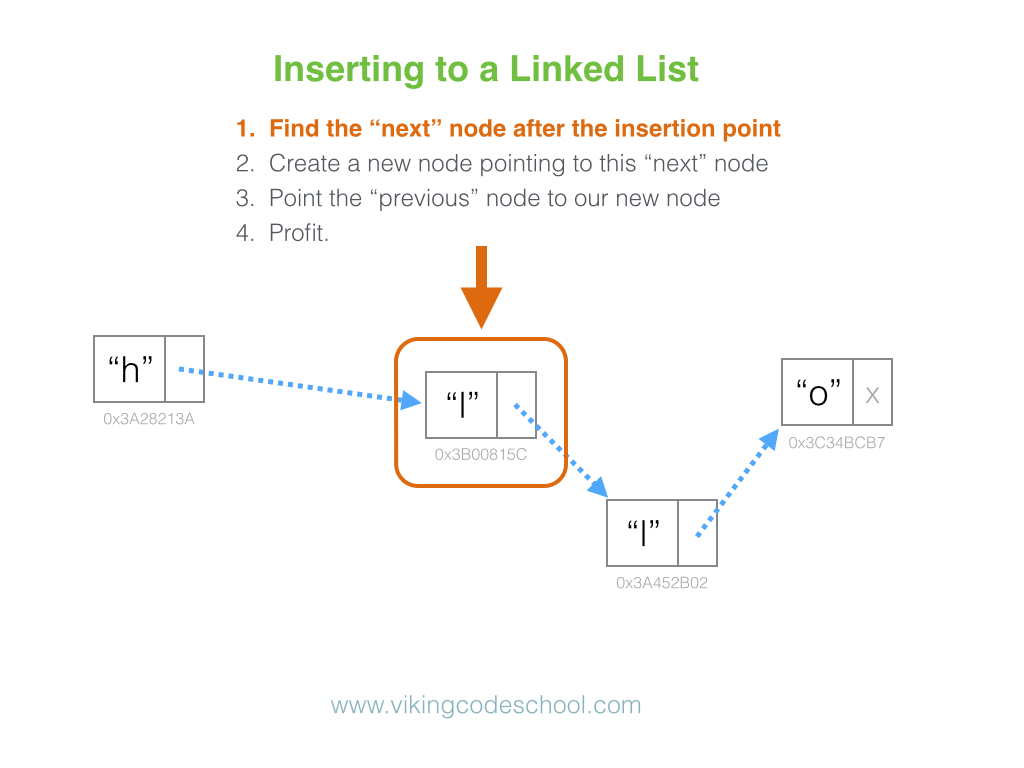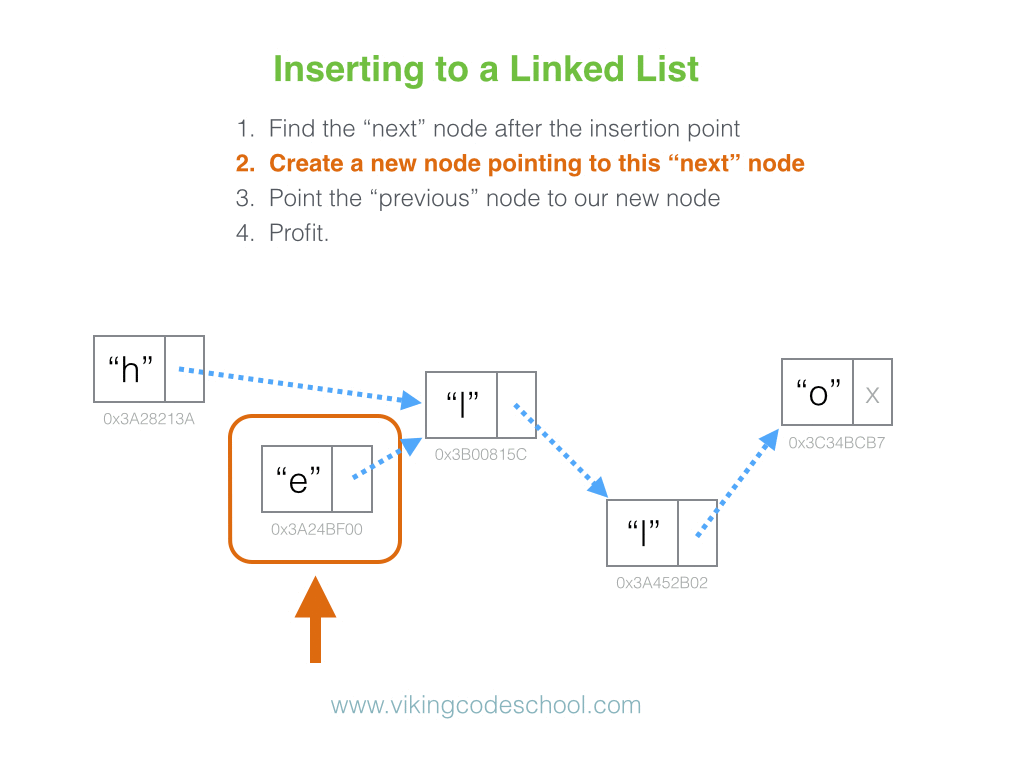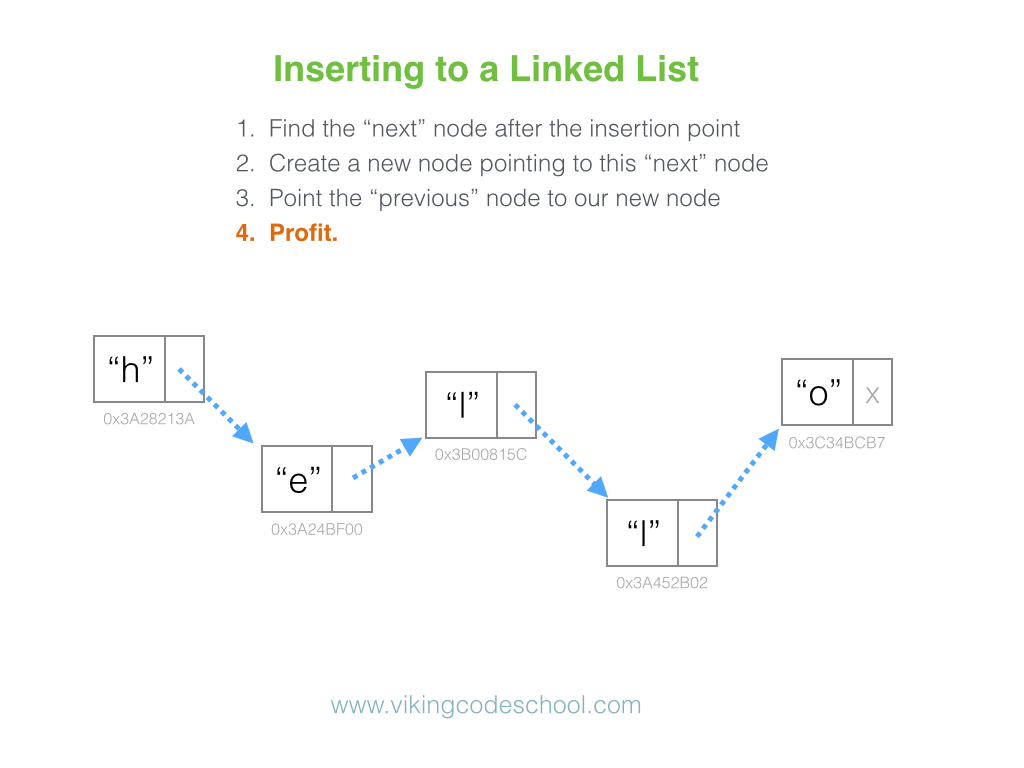
A Singly Linked List is a linear collection of data elements, called nodes pointing to the next node by means of pointer. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence.
Linked Lists are among the simplest and most common data structures because it allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(n) O(n) O(1) O(1)
The code
The Doubly Linked List
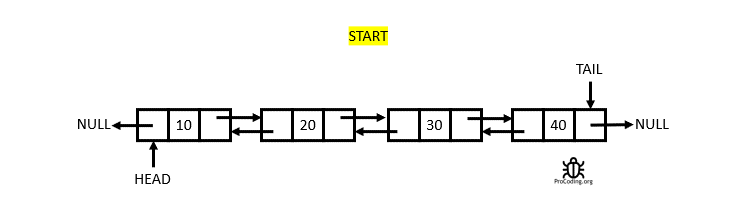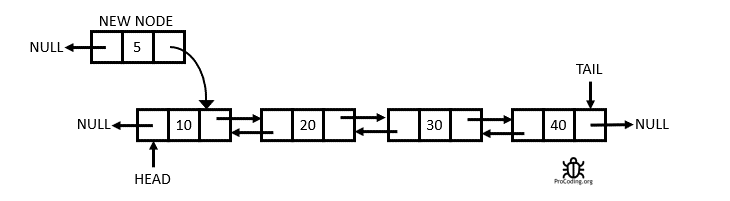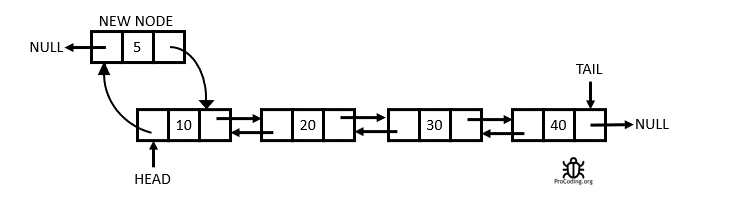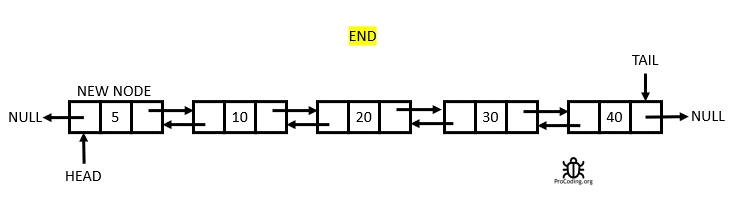
A Doubly Linked List is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains two fields, called links, that are references to the previous and to the next node in the sequence of nodes. From Wikipedia
Having two node links allow traversal in either direction but adding or removing a node in a doubly linked list requires changing more links than the same operations on a Singly Linked List.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(n) O(n) O(1) O(1)
The code
The Stack
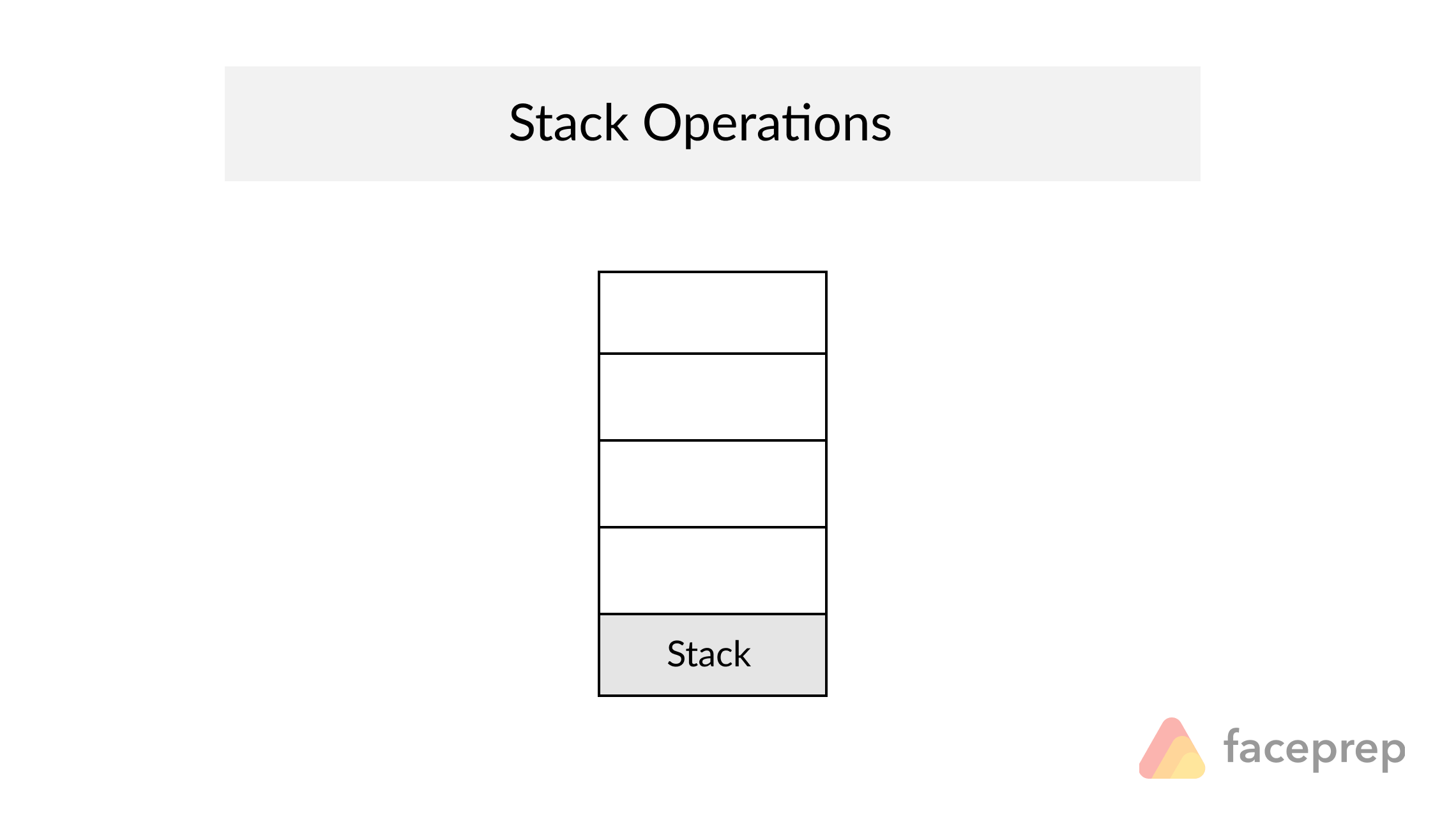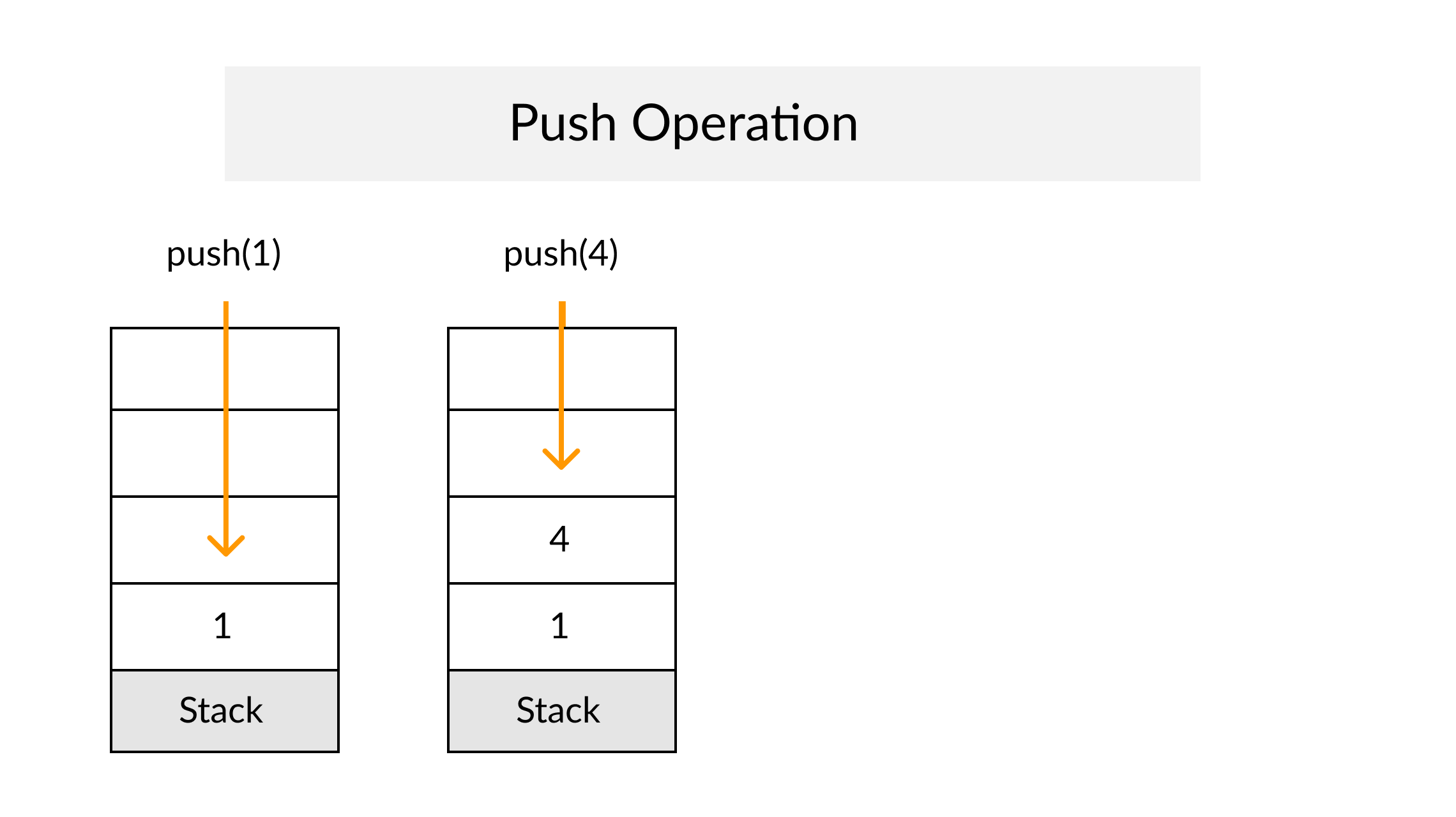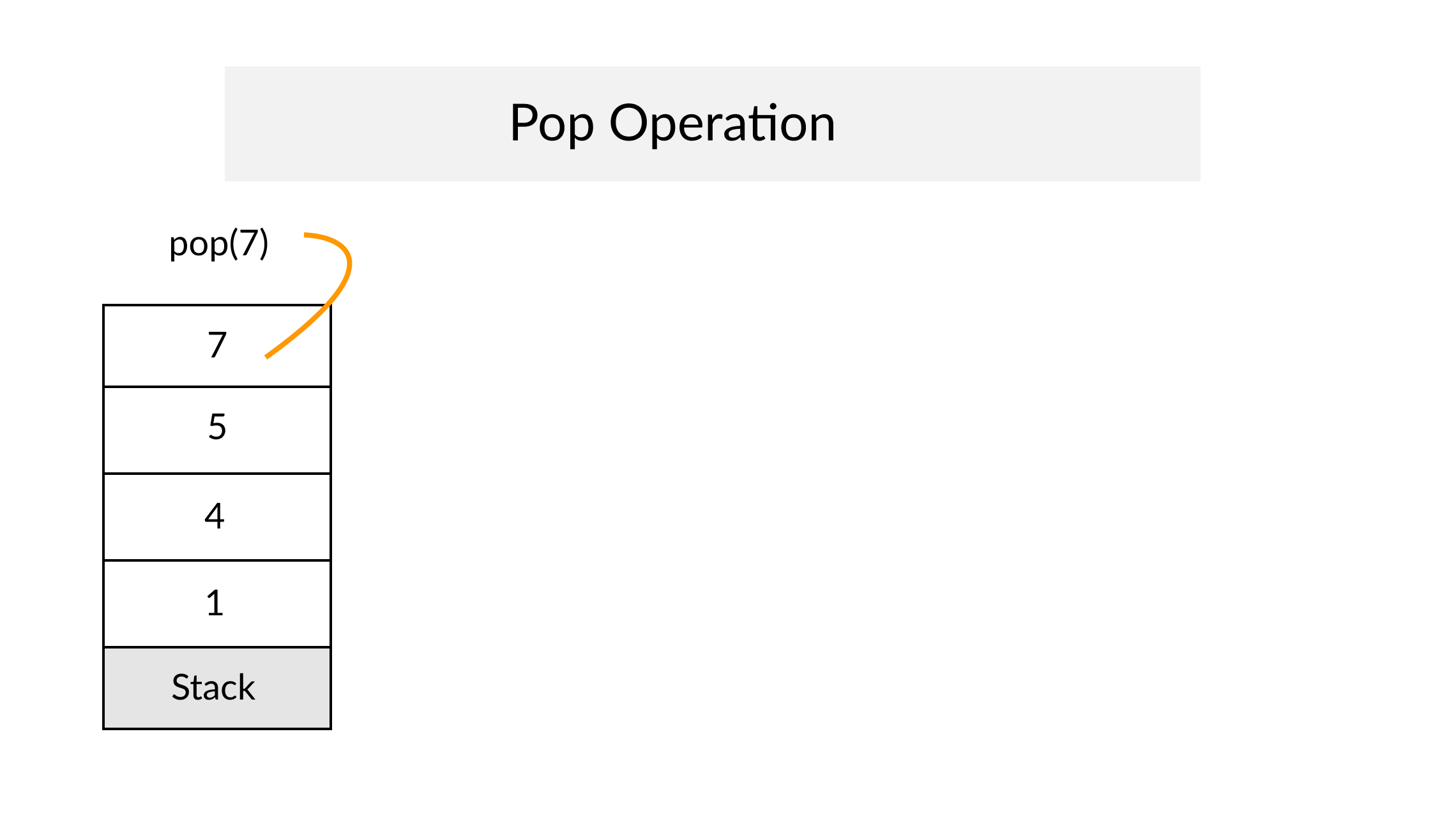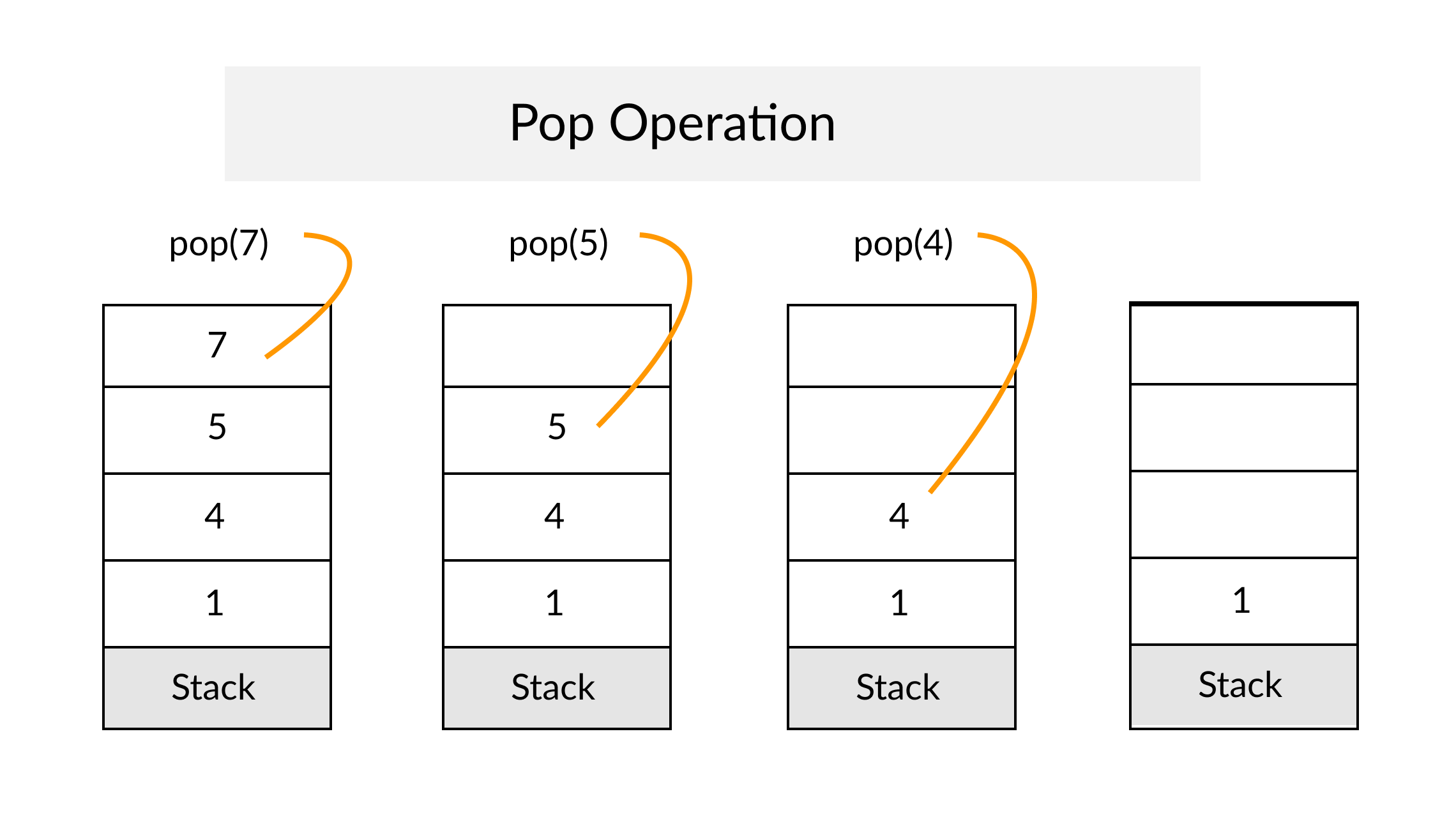
Definition
A Stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two principal operations: push, which adds an element to the collection, and pop, which removes the most recently added element that was not yet removed. The order in which elements come off a Stack gives rise to its alternative name, LIFO (for last in, first out). From Wikipedia
A Stack often has a third method peek which allows to check the last pushed element without popping it.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(n) O(n) O(1) O(1)
The code
The Queue
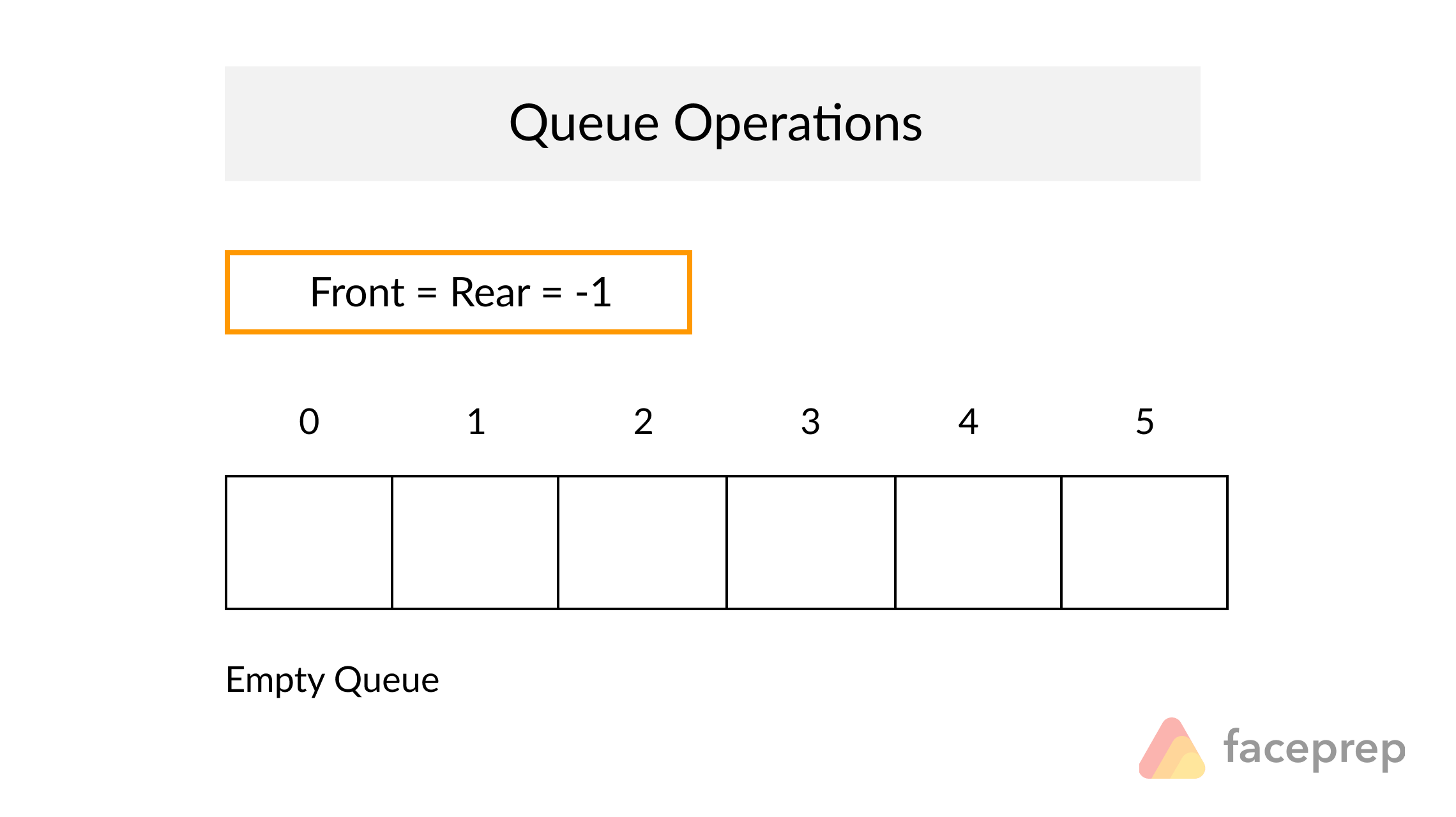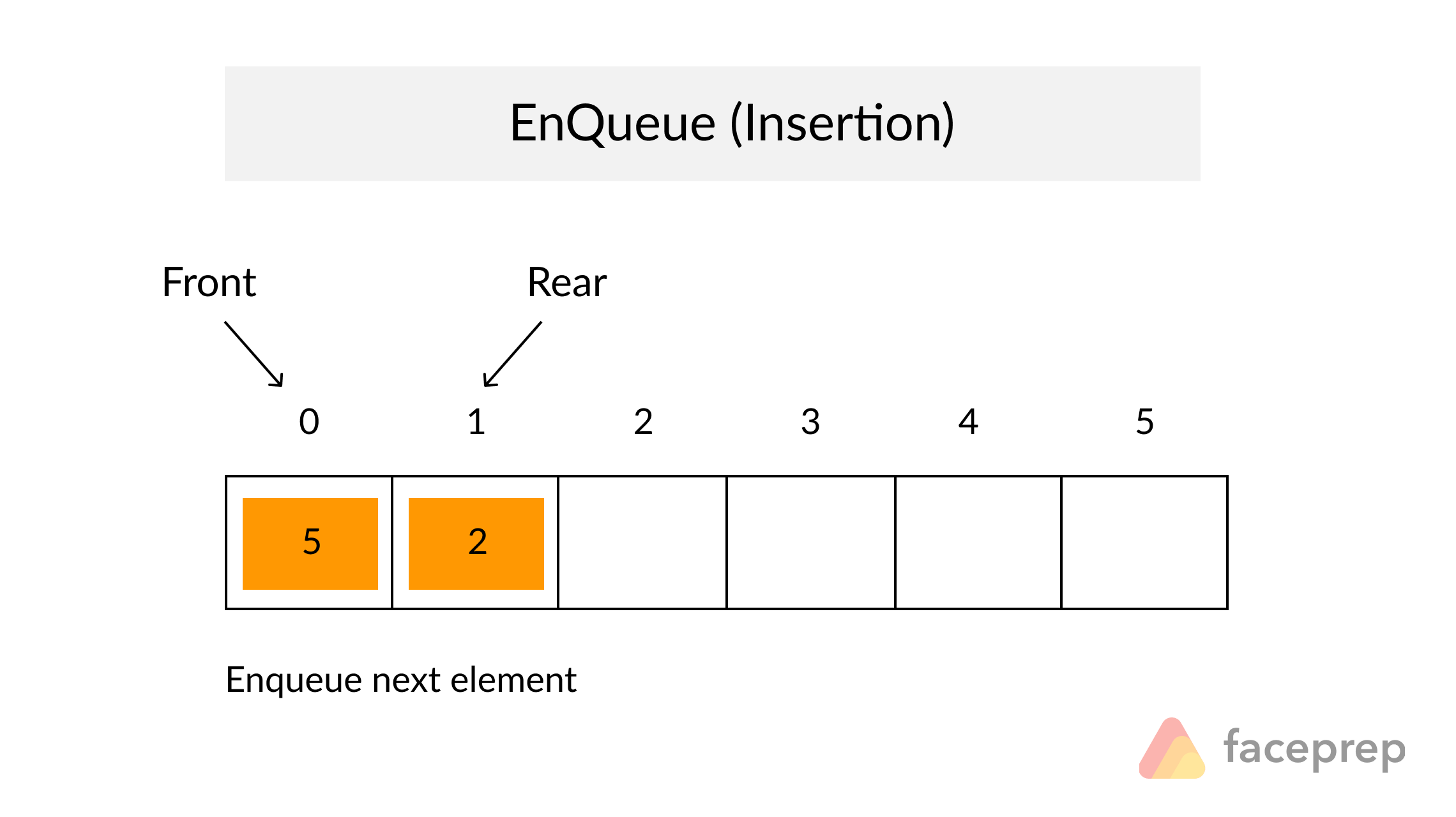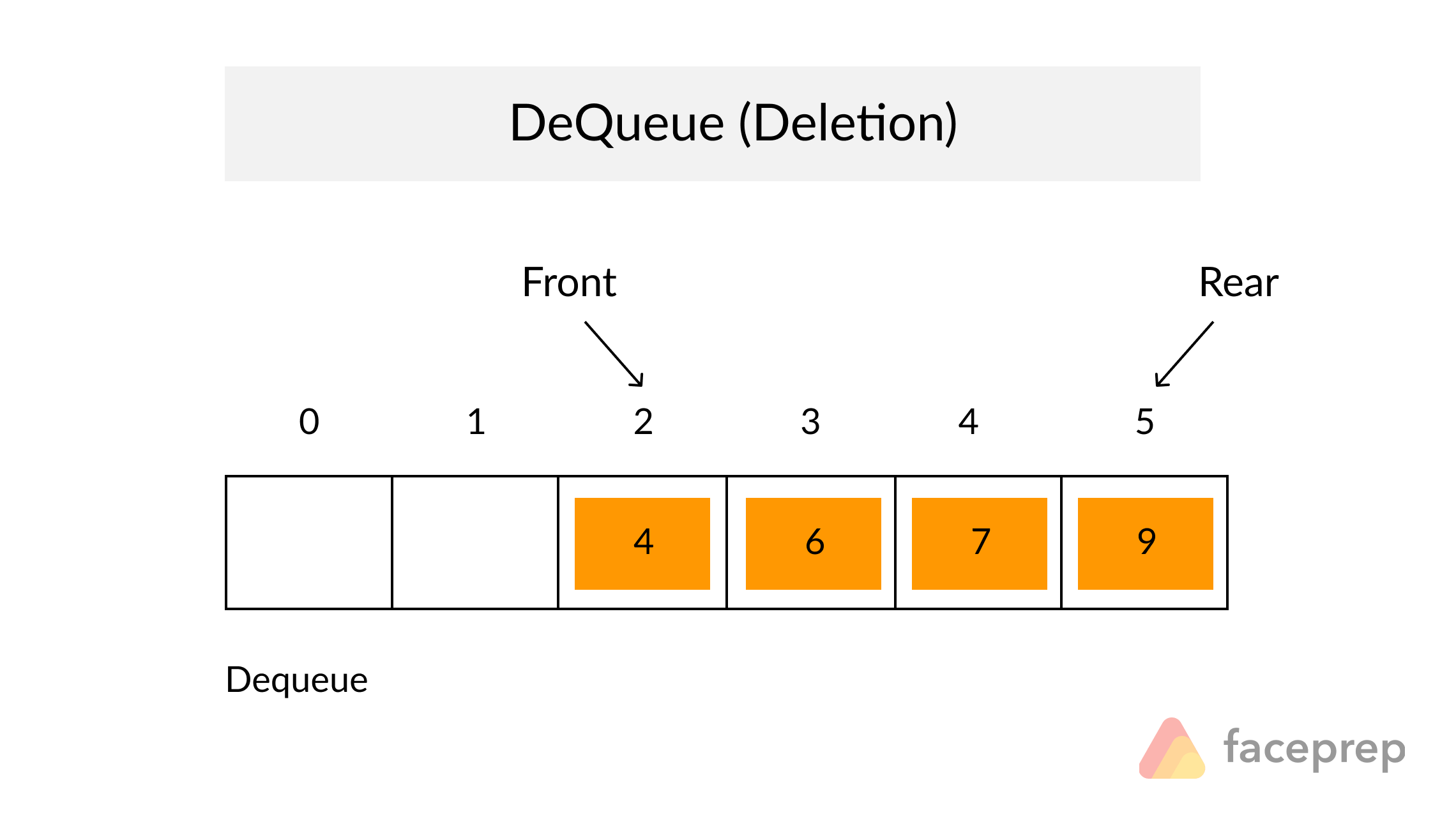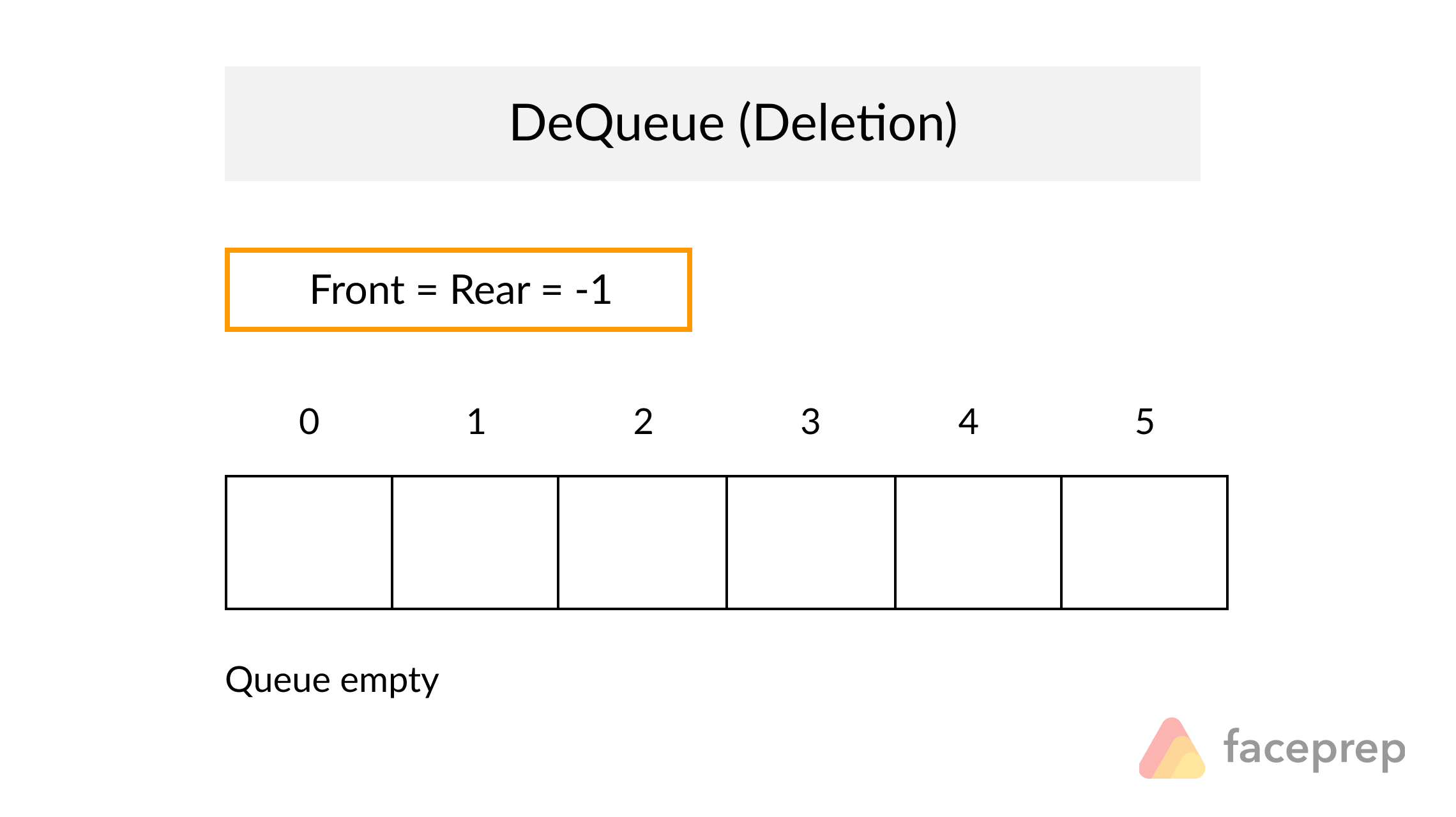
A Queue is a particular kind of abstract data type or collection in which the entities in the collection are kept in order and the principal operations are the addition of entities to the rear terminal position, known as enqueue, and removal of entities from the front terminal position, known as dequeue. This makes the Queue a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the Queue will be the first one to be removed.
As for the Stack data structure, a peek operation is often added to the Queue data structure. It returns the value of the front element without dequeuing it.
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(n) O(n) O(1) O(n)
The code
The Tree
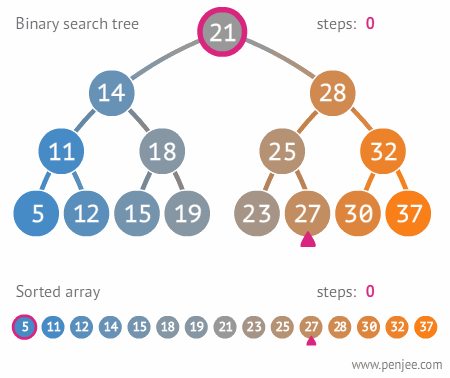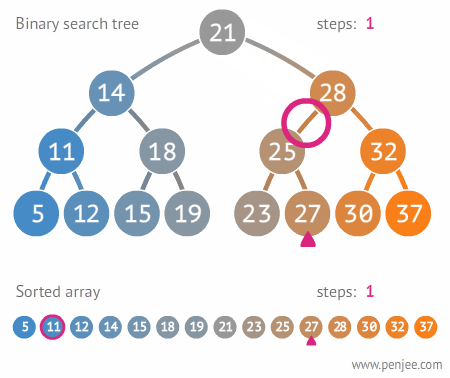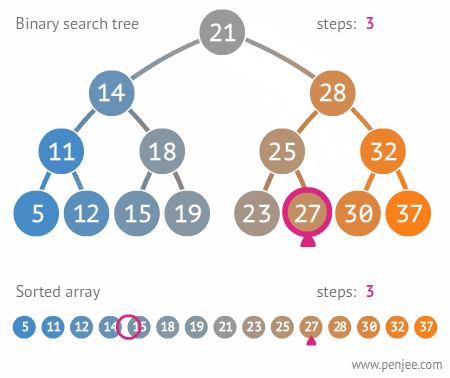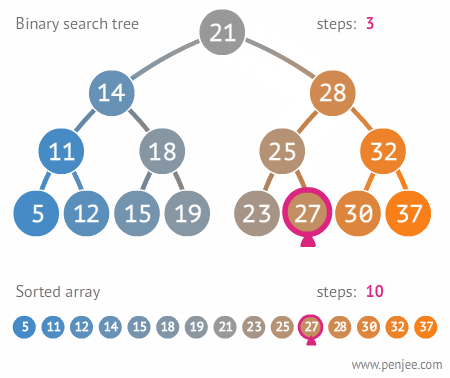
A Tree is a widely used data structure that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and subtrees of children with a parent node. A tree data structure can be defined recursively as a collection of nodes (starting at a root node), where each node is a data structure consisting of a value, together with a list of references to nodes (the “children”), with the constraints that no reference is duplicated, and none points to the root node. From Wikipedia
Complexity
Average
Access Search Insertion Deletion
O(n) O(n) O(n) O(n)
To get a full overview of the time and space complexity of the Tree data structure, have a look to this excellent Big O cheat sheet.
The Graph
A Graph data structure consists of a finite (and possibly mutable) set of vertices or nodes or points, together with a set of unordered pairs of these vertices for an undirected Graph or a set of ordered pairs for a directed Graph. These pairs are known as edges, arcs, or lines for an undirected Graph and as arrows, directed edges, directed arcs, or directed lines for a directed Graph. The vertices may be part of the Graph structure, or may be external entities represented by integer indices or references.
- A graph is any collection of nodes and edges.
- Much more relaxed in structure than a tree.
- It doesn’t need to have a root node (not every node needs to be accessible from a single node)
- It can have cycles (a group of nodes whose paths begin and end at the same node)
- Cycles are not always “isolated”, they can be one part of a larger graph. You can detect them by starting your search on a specific node and finding a path that takes you back to that same node.
- Any number of edges may leave a given node
- A Path is a sequence of nodes on a graph
Cycle Visual
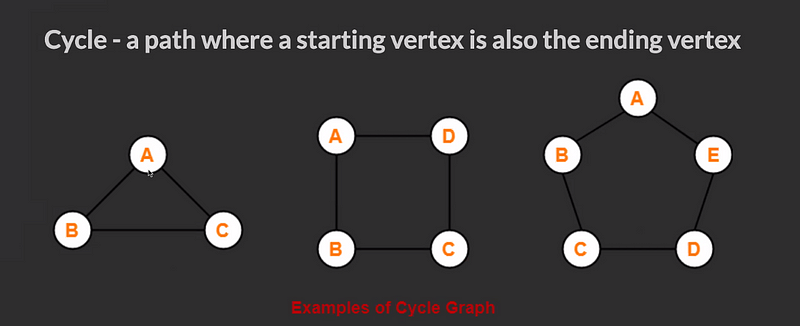
Representation
There are different ways of representing a graph, each of them with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are the main 2:
Adjacency list: For every vertex a list of adjacent vertices is stored. This can be viewed as storing the list of edges. This data structure allows the storage of additional data on the vertices and edges.
Adjacency matrix: Data are stored in a two-dimensional matrix, in which the rows represent source vertices and columns represent destination vertices. The data on the edges and vertices must be stored externally.
Graph
The code
If you found this guide helpful feel free to checkout my GitHub/gists where I host similar content:
bgoonz’s gists
Instantly share code, notes, and snippets. Web Developer, Electrical Engineer JavaScript | CSS | Bootstrap | Python |…gist.github.com
bgoonz — Overview
Web Developer, Electrical Engineer JavaScript | CSS | Bootstrap | Python | React | Node.js | Express | Sequelize…github.com
Or Checkout my personal Resource Site:
Discover More:
Web-Dev-Hub
Memoization, Tabulation, and Sorting Algorithms by Example Why is looking at runtime not a reliable method of…bgoonz-blog.netlify.app
By Bryan Guner on March 5, 2021.
Exported from Medium on August 31, 2021.
